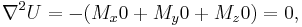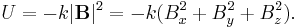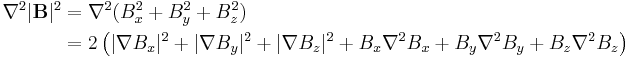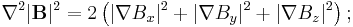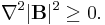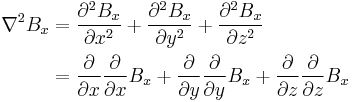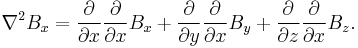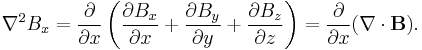Earnshaw's theorem
Earnshaw's theorem states that a collection of point charges cannot be maintained in a stable stationary equilibrium configuration solely by the electrostatic interaction of the charges. This was first proven by British mathematician Samuel Earnshaw in 1842. It is usually referenced to magnetic fields, but originally applied to electrostatic fields. It applies to the classical inverse-square law forces (electric and gravitational) and also to the magnetic forces of permanent magnets and paramagnetic materials or any combination, (but not diamagnetic materials).
Contents |
Explanation
Informally, the case of a point charge in an arbitrary static electric field is a simple consequence of Gauss's law. For a particle to be in a stable equilibrium, small perturbations ("pushes") on the particle in any direction should not break the equilibrium; the particle should "fall back" to its previous position. This means that the force field lines around the particle's equilibrium position should all point inwards, towards that position. If all of the surrounding field lines point towards the equilibrium point, then the divergence of the field at that point must be negative (i.e. that point acts as a sink). However, Gauss's Law says that the divergence of any possible electric force field is zero in free space. In mathematical notation, an electrical force 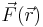 deriving from a potential
deriving from a potential 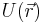 will always be divergenceless (satisfy Laplace's equation):
will always be divergenceless (satisfy Laplace's equation):
Therefore, there are no local minima or maxima of the field potential in free space, only saddle points. A stable equilibrium of the particle cannot exist and there must be an instability in at least one direction.
To be completely rigorous, strictly speaking, the existence of a stable point does not require that all neighboring force vectors point exactly toward the stable point; the force vectors could spiral in towards the stable point, for example. One method for dealing with this invokes the fact that, in addition to the divergence, the curl of any electric field in free space is also zero (in the absence of any magnetic currents).
This theorem also states that there is no possible static configuration of ferromagnets which can stably levitate an object against gravity, even when the magnetic forces are stronger than the gravitational forces.
Earnshaw's theorem has even been proven for the general case of extended bodies, and this is so even if they are flexible and conducting, provided they are not diamagnetic,[1][2] as diamagnetism constitutes a (small) repulsive force, but no attraction.
There are, however, several exceptions to the rule's assumptions which allow magnetic levitation.
Loopholes
Earnshaw's theorem has no exceptions for unmoving permanent ferromagnets. However, moving ferromagnets, certain electromagnetic systems, pseudo-levitation and diamagnetic materials are areas to which Earnshaw's theorem doesn't apply and thus can seem to be exceptions, though in fact these exploit the constraints of the theorem.
Spinning ferromagnets (such as the Levitron) can—while spinning—magnetically levitate using only permanent ferromagnets. Note, since this is spinning, this is not a non-moving ferromagnet.
Switching electromagnets polarity allows for keeping a system levitating by the continuous expenditure of energy. An example of this is maglev trains
Pseudo-levitation constrains the movement of the magnets usually using some form of a tether or wall. This works because the theorem shows only that there is some direction in which there will be an instability. Limiting movement in that direction allows for levitation with fewer than the full 3 dimensions available for movement (note that the theorem is proven for 3 dimensions, not 1D or 2D).
Diamagnetic materials are excepted because they exhibit only repulsion against the magnetic field, whereas the theorem requires materials that have both repulsion and attraction. A fun example of this is the famous levitating frog (see diamagnetism).
Impact on physics
Earnshaw’s theorem, in addition to the fact that configurations of classical charged particles orbiting one another are also unstable due to electromagnetic radiation, mean that even dynamic systems of charges are unstable, long term. This, for quite some time led to the puzzling question of why matter stays together as much evidence was found that matter was held together electromagnetically.
These questions eventually pointed the way to quantum mechanical explanations of the structure of the atom, and it turns out that the Pauli exclusion principle is responsible for holding bulk matter in a rigid shape.
Proofs for magnetic dipoles
Introduction
While a more general proof may be possible, three specific cases are considered here. The first case is a magnetic dipole of constant magnitude that has a fast (fixed) orientation. The second and third cases are magnetic dipoles where the orientation changes to remain aligned either parallel or antiparallel to the field lines of the external magnetic field. In paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials the dipoles are aligned parallel and antiparallel to the field lines, respectively.
Background
The proofs considered here are based on the following principles.
The energy U of a magnetic dipole with a magnetic dipole moment M in an external magnetic field B is given by
The dipole will only be stably levitated at points where the energy has a minimum. The energy can only have a minimum at points where the Laplacian of the energy is greater than zero. That is, where
Finally, because both the divergence and the curl of a magnetic field are zero (in the absence of current or a changing electric field), the Laplacians of the individual components of a magnetic field are zero. That is,
This is proved at the very end of this article as it is central to understanding the overall proof.
Summary of proofs
For a magnetic dipole of fixed orientation (and constant magnitude) the energy will be given by
where 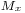 ,
, 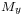 and
and 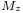 are constant. In this case the Laplacian of the energy is always zero,
are constant. In this case the Laplacian of the energy is always zero,
so the dipole can have neither an energy minimum or an energy maximum. That is, there is no point in free space where the dipole is either stable in all directions or unstable in all directions.
Magnetic dipoles aligned parallel or antiparallel to an external field with the magnitude of the dipole proportional to the external field will correspond to paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials respectively. In these cases the energy will be given by
where k is a constant greater than zero for paramagnetic materials and less than zero for diamagnetic materials.
In this case, it will be shown that
which, combined with the constant k, shows that paramagnetic materials can have energy maxima but not energy minima and diamagnetic materials can have energy minima but not energy maxima. That is, paramagnetic materials can be unstable in all directions but not stable in all directions and diamagnetic materials can be stable in all directions but not unstable in all directions. Of course, both materials can have saddle points.
Finally, the magnetic dipole of a ferromagnetic material (a permanent magnet) that is aligned parallel or antiparallel to a magnetic field will be given by
so the energy will be given by
but this is just the square root of the energy for the paramagnetic and diamagnetic case discussed above and, since the square root function is monotonically increasing, any minimum or maximum in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic case will be a minimum or maximum here as well. There are, however, no known configurations of permanent magnets that stably levitate so there may be other reasons not discussed here why it is not possible to maintain permanent magnets in orientations antiparallel to magnetic fields (at least not without rotation—see Levitron).
Detailed proofs
Earnshaw's theorem was originally formulated for electrostatics (point charges) to show that there is no stable configuration of a collection of point charges. The proofs presented here for individual dipoles should be generalizable to collections of magnetics dipoles because they are formulated in terms of energy which is additive. A rigorous treatment of this topic, however, is currently beyond the scope of this article.
Fixed-orientation magnetic dipole
It will be proven that at all points in free space
The energy U of the magnetic dipole M in the external magnetic field B is given by
The Laplacian will be
Expanding and rearranging the terms (and noting that the dipole M is constant) we have
but the Laplacians of the individual components of a magnetic field are zero in free space (not counting electromagnetic radiation) so
which completes the proof.
Magnetic dipole aligned with external field lines
The case of a paramagnetic or diamagnetic dipole is considered first. The energy is given by
Expanding and rearranging terms,
but since the Laplacian of each individual component of the magnetic field is zero,
and since the square of a magnitude is always positive,
As discussed above, this means that the Laplacian of the energy of a paramagnetic material can never be positive (no stable levitation) and the Laplacian of the energy of a diamagnetic material can never be negative (no instability in all directions).
Further, because the energy for a dipole of fixed magnitude aligned with the external field will be the square root of the energy above, the same analysis applies.
Laplacian of individual components of a magnetic field
It is proven here that the Laplacian of each individual component of a magnetic field is zero. This shows the need to invoke the properties of magnetic fields that the divergence of a magnetic field is always zero and the curl of a magnetic field is zero in free space. (That is, in the absence of current or a changing electric field.) See Maxwell's equations for a more detailed discussion of these properties of magnetic fields.
Consider the Laplacian of the x component of the magnetic field
Because the curl of B is zero, 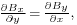 and
and 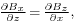 so we have
so we have
But since 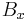 is continuous, the order of differentiation doesn't matter giving
is continuous, the order of differentiation doesn't matter giving
The divergence of B is zero, 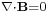 , so
, so
The Laplacian of the y component of the magnetic field 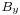 field and the Laplacian of the z component of the magnetic field
field and the Laplacian of the z component of the magnetic field 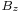 can be calculated analogously. Alternatively, one can use the identity
can be calculated analogously. Alternatively, one can use the identity 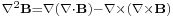 , where both terms in the parentheses vanish.
, where both terms in the parentheses vanish.
Notes
- ^ Gibbs, Philip & Geim, Andre. "Is Magnetic Levitation Possible?". High Field Magnet Laboratory. http://www.ru.nl/hfml/research/levitation/diamagnetic/levitation_possible/. Retrieved 2010-01-04.
- ^ Earnshaw, S., On the nature of the molecular forces which regulate the constitution of the luminferous ether., Trans. Camb. Phil. Soc., 7, pp 97-112 (1842)
References
- Earnshaw, Samuel (1842). "On the Nature of the Molecular Forces which Regulate the Constitution of the Luminiferous Ether". Trans. Camb. Phil. Soc. 7: 97–112.
- Scott, W. T. (1959). "Who Was Earnshaw?". American Journal of Physics 27: 418. Bibcode 1959AmJPh..27..418S. doi:10.1119/1.1934886.
External links
- "Is magnetic levitation possible?", a discussion of Earnshaw's theorem and its consequences for levitation, along with several ways to levitate with electromagnetic fields
- Biography and other information about Samuel Earnshaw
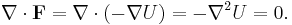
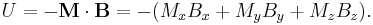
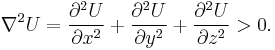
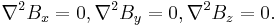
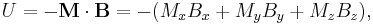
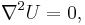
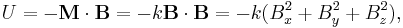
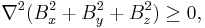
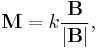
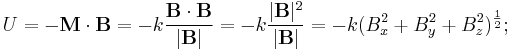
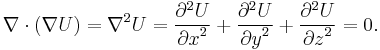
![\nabla^2 U = -\left[\begin{align}
&{\partial^2 (M_x B_x %2B M_y B_y %2B M_z B_z) \over {\partial x}^2} %2B\\
&{\partial^2 (M_x B_x %2B M_y B_y %2B M_z B_z) \over {\partial y}^2} %2B\\
&{\partial^2 (M_x B_x %2B M_y B_y %2B M_z B_z) \over {\partial z}^2}\end{align}\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/4a3bcb3a48d03e5d0ae9a59001e6dc54.png)
![\begin{align}
\nabla^2 U &= -\left[\begin{align}
&M_x\left({\partial^2 B_x \over {\partial x}^2} %2B
{\partial^2 B_x \over {\partial y}^2} %2B
{\partial^2 B_x \over {\partial z}^2}\right) %2B\\
&M_y\left({\partial^2 B_y \over {\partial x}^2} %2B
{\partial^2 B_y \over {\partial y}^2} %2B
{\partial^2 B_y \over {\partial z}^2}\right) %2B\\
&M_z\left({\partial^2 B_z \over {\partial x}^2} %2B
{\partial^2 B_z \over {\partial y}^2} %2B
{\partial^2 B_z \over {\partial z}^2}\right)\end{align}\right]\\
&= -(M_x \nabla^2 B_x %2B M_y \nabla^2 B_y %2B M_z \nabla^2 B_z)
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/73c89900d2581f004535d2fe2c1b734e.png)